Investigating the effect of water vapour and residual methanol on the anode of HTPEM fuel cell
An investigation with different anode fuel compositions and results in terms of performance and impedance analysed. During the initial 1000 h, cell was tested with pure hydrogen under varying current densities of 0.2 A cm-2 and 0.6 A cm-2, followed by hydrogen mixed with 15 % water vapour and then with 1 % methanol. The degradation at higher current density is more severe than at lower current density. However, on switching from higher to lower current density, the effect is reversible and the performance is improved. The addition of water vapour in the feed improves the performance at high current densities, which suggest an improvement of total cell resistance also supported by the impedance comparison. There is no or minimal variation in performance with the introduction of 1 % methanol along with water vapour in the anode feed at 0.2 A cm-2 and 0.6A cm-2.
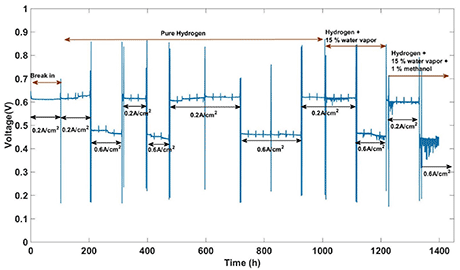
Fig: 1 Voltage profile with varying fuel composition on the anode
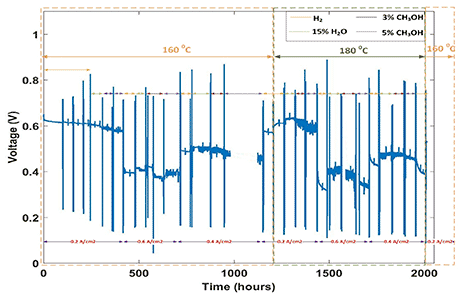
Investigating the temperature and current density effect on HTPEM performance with reformate feed (residual methanol (3 % and 5 %) and water vapour (15 %))
The test was performed at two different temperatures (160 °C and 180 °C) and three different current densities (0.2 A cm-2, 0.4 A cm-2 and 0.6 A cm-2). The results suggests partial mitigation of methanol
effects in the presence of water vapour. The addition of water vapour in the feed improves the performance at high current densities and higher temperature. An improvement in the total cell resistance supports the voltage improvement under a specific current density. There is no or minimal variation in performance with the introduction of 3 % and 5 % methanol along with water vapour in the anode feed. The overall degradation over a period of 2100 h is 39-μV h-1.
Publication/Presentation
- “INVESTIGATING THE EFFECT OF WATER VAPOR AND RESIDUAL METHANOL ON THE ANODE OF HIGH TEMPERATURE PEM FUEL CELL” presented at European Fuel Cell Technology & Applications Conference - Piero Lunghi Conference December 16-18, 2015, Naples, Italy.
- “Investigating the temperature and current density effect on HTPEM performance with reformate feed (residual methanol (3 % and 5 %) and water vapour (15 %))” to be submitted to Applied energy.